How Does Raid 5 Have 2 Reads
RAID is a technology that'south used to raise operation, storage efficiency, and fault tolerance. RAID stands for redundant array of independent disks, and as the name suggests, this technology is a combination of two or more disks that piece of work in parallel to provide a range of benefits. The way these devices interact or work with each other depends on the way they're configured. RAID configurations or levels come in different flavors offer different benefits, so individuals and organizations choose the RAID level that best meets their goals and needs. In this article, we'll be comparing RAID 5 and RAID half-dozen to empathise which of the two you should choose in a given scenario.
What is RAID v?
Wikimedia
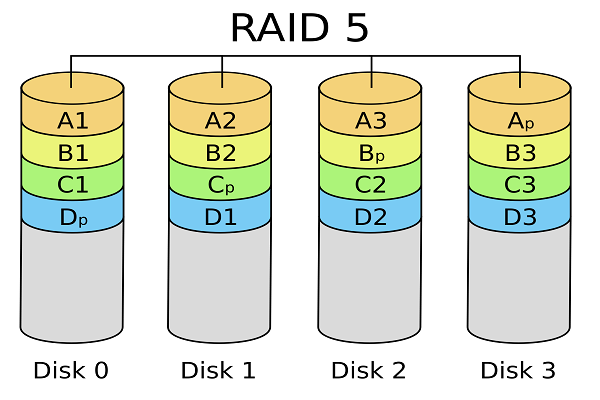
RAID five is a configuration that uses disk striping with parity. In striping, consecutive data blocks are stored across different devices for quick reading, while parity handles the mistake checking.
In others, all the data and its associated parity are split across all the bachelor disks evenly to ensure that the failure of a single deejay doesn't bring downwards operations and also to make it easy to reconstruct data in the event of a failure.
Advantages
The advantages of RAID 5 are:
- Practiced throughput and performance.
- It provides data redundancy.
- This configuration is highly stable and reliable.
- It can quickly rebuild a failed drive.
- Efficient use of bachelor space.
- Drives can be hot-swapped to avoid downtime.
- One of the most popular RAID implementations.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages of RAID five are:
- Information technology cannot withstand ii simultaneous disk failures.
- Writing is slow compared to other configurations because of parity.
- Data restoration tin have time.
- Complex to implement.
- Information is lost when ii or more disks neglect.
What is RAID 6?
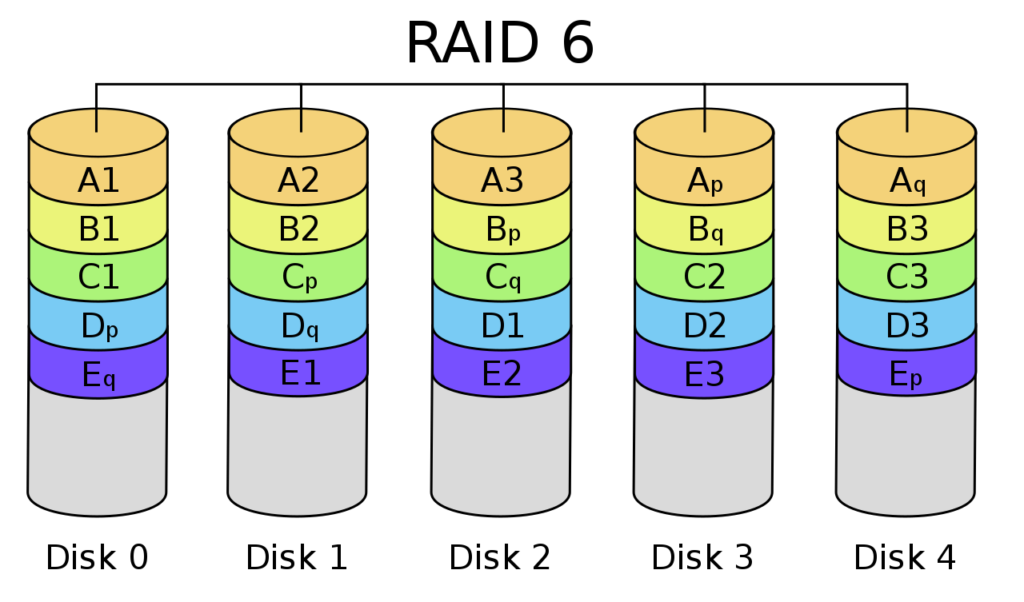
RAID 6 is like to RAID 5, except that it uses double parity for enhanced error tolerance. The first parity is like to RAID 5 (XOR part), while the 2d parity is a lot more complex.
Wikimedia
And so, fifty-fifty if two disks fail simultaneously, RAID 6 can reconstruct the information with the double parity. This makes RAID 6 highly secure and error-tolerant.
Advantages
The advantages of RAID 6 are:
- High redundancy and fault tolerance.
- Reasonably fast read operations.
- Splendid data accessibility.
- Highly secure.
- Supports up to two disk failures.
Disadvantages
The disadvantages are:
- Write transactions are very wearisome due to double parity.
- Complex to implement.
- Restoring takes a lot of fourth dimension.
- Data is completely lost when three or more than disks fail simultaneously.
This should give yous a fair thought of RAID v and RAID half dozen. Permit's see the differences and applications of each.
Differences between RAID 5 and RAID 6
Some of the cardinal differences between RAID 5 and RAID half dozen are:
Features | RAID five | RAID half dozen |
| Minimum number of disks | 3 | 4 |
| Recovery from two disk failures | No | Aye |
| Software/Hardware RAID configuration | Both | Hardware but |
| Implementation cost | Less | More than |
| Write performance | Slow | Slower |
| Parity | Single | Double |
| Maximum drives | 32 | 32 |
| Read performance | Fast | Fast |
In general, RAID 6 offers greater information protection and fault tolerance than RAID 5, but at the aforementioned fourth dimension, it'south write functioning is slower than RAID five because of double parity, though the read operations are equally fast.
RAID v, on the other paw, is cheaper to implement and provides more than optimized storage than RAID six.
Real-world applications
Allow'south await at some real-world situations to understand which RAID level to utilize when.
Shoestring budget
If you're on a upkeep, RAID 5 is your hands-down pick considering information technology requires only iii disks and tin can exist implemented through software. Also, RAID 5 offers a good residue between performance, storage, and throughput, without putting a ton of pressure level on your finances.
High-availability applications
RAID 6 is the best selection for critical applications that require high availability, such every bit online client service portals, because of its loftier mistake tolerance.
File and application servers
RAID five is a good choice for file and application servers such every bit email and news servers as they provide fast reads and a somewhat slower write, which is insignificant in these scenarios.
Good storage and operation are besides added advantages that make this RAID level ideal for file and server applications.
More than reads than writes
Employ RAID half-dozen for standard spider web servers as there is more read than write transactions in these applications.
This RAID level is non recommended for heavy write-based applications such equally database servers because the double parity increases write time.
Quicker recovery
When you want to recover your data apace, RAID 5 is a faster selection than RAID 6, every bit the latter can accept a long fourth dimension to reconstruct the information because of double parity. Nonetheless, if you don't heed the extra time only want better fault tolerance, get for RAID 6.
Archiving and backup
RAID 6 works well for archiving and backups and on servers with large capacities as it reduces the chances for data loss due to double disk failures.
Hardware/software implementation
RAID 5 can exist implemented with both hardware and software, while RAID vi is a complete hardware implementation. Needless to say, having a dedicated hardware controller costs more coin and entails a circuitous setup.
Efficient storage capacity
If you're looking for efficient storage capacity, RAID 5 is your selection as information technology balances storage, performance, security, and throughput well. Also, you only need a minimum of three disks to implement RAID 5 as opposed to four drives of RAID 6.
Disk failure
When two disks neglect, all the associated information is lost in RAID 5, whereas RAID 6 tin handle a 2-disk failure well. However, all information will be lost in RAID 6 when three or more disks fail.
That's why support your information, as RAID levels are never an alternative for data backups.
RAID five and RAID half dozen: Similar but different
To conclude, both RAID 5 and RAID 6 are similar as RAID 6 is nil but an extension of RAID 5 with an extra parity. Only this extra parity provides high fault tolerance even when two disks fail, thereby making RAID 6 ideal for business-critical applications. But RAID 6 is more expensive every bit information technology requires more storage and a dedicated hardware controller, whereas RAID 5 gives a skilful balance of storage, efficiency, and performance.
Both RAID levels take comparable read and write speeds, though RAID half dozen is slightly slower for writing considering of its double parity.
In all, both these RAID levels are avant-garde implementations that provide a ton of benefits. And then, choose the one that best fits your needs.
If you lot take implemented one over the other, delight share your experience in the comments section.
Featured prototype: Shutterstock
More RAID levels articles
- Hackers: the New Ghosts in the Machine
- RAID x vs. RAID 5: When to use each level and why
- RAID one vs. RAID 5: When to use each level and why
- RAID 0 vs. RAID one: When to use each level and why
- Hardware RAID vs. software RAID: Pros and cons for each
Source: https://techgenix.com/raid-5-vs-raid-6/
Belum ada Komentar untuk "How Does Raid 5 Have 2 Reads"
Posting Komentar